What is Patchworks?
Spatially explicit, visual, dynamic
Patchworks is a spatially explicit forest modeling application that is built on a dynamic and configurable platform. Patchworks is highly visual and highly interactive, while also supporting a batch system for production modeling tasks. Patchworks features an intuitive point-and-click interface and makes extensive use of easy-to-follow wizards. For power users, it offers an object-oriented scripting language, a rich API, and is well supported by automated code generators.
Advanced analytical operators
Patchworks unleashes the power and flexibility of advanced analytical operators on forest management problems in a way that naturally expresses the true nature of the issues. Simulation modeling is best used to shine a light of understanding on complex problems, and Patchworks facilitates this with its elegant and transparent modeling approaches.
Strategic and operational
Most importantly, Patchworks unifies the challenge of analyzing long-term goals while choosing short-term actions. Planning models that generate strategic answers without considering location and then apply an add-on layout tool as an afterthought end up violating their initial planning objectives, and miss out on finding balanced, best-outcome solutions. Patchworks is a long-term strategic modeling platform, and it works with operational detail, all at the same time. This means that the costs and impacts of implementing an operational layout are fully considered during the strategic planning phase, ensuring that treatments, budgets and locations harmonize with each other, with no surprises to come along later.
Flexible Stand Dynamics
Mimic reality
At the heart of every wood supply model are the descriptions of how stands grow, change, and respond to management actions. It is crucially important to represent stand dynamics within the model to closely mimic natural developments in the real world. Patchworks excels at allowing you to set up stand dynamics according to your specifications, using your nomenclature and whatever level of complexity is required.
Flexible and comprehensive
Patchworks provides a flexible and comprehensive way to describe stand dynamic characteristics using the ForestModel XML language. ForestModel XML is fully generalized and adaptable to your forest types and silvicultural programs. Even-aged, thinning, selection, shelterwood, underplanting, mid-rotation partial harvest, understory removal: ForestModel has the flexibility to represent all kinds of actions and responses.
Build your ForestModel XML file using one of our MS Excel templates, convert from an existing model using one of our translators, or export from your DBMS into XML format.
The MatrixBuilder tool combines the ForestModel with your forest inventory, producing a compact set of inputs optimized for speedy processing. The MatrixBuilder can also work with outputs from the intelligent dissolve tool to reduce sliver polygons without losing accuracy: forest-level summaries remain the same before and after dissolving.
Ready for LiDAR
Patchworks is ready and able to fully utilize enhanced information provided by LiDAR-based inventories, including the ability to set up unique sets of growth curves and treatment options for each individual stand.
Spatial Modeling
The Patchworks software provides a number of effective, innovative mechanisms to control the allocation of management treatments and the retention of forest structures. Most of the spatial controls are implemented as goals that can be met by the careful arrangement of management treatments. The modeling system has been designed for maximum flexibility and expressiveness, allowing you to mix and match controls as needed to represent your forest planning problem.
Patch Targets
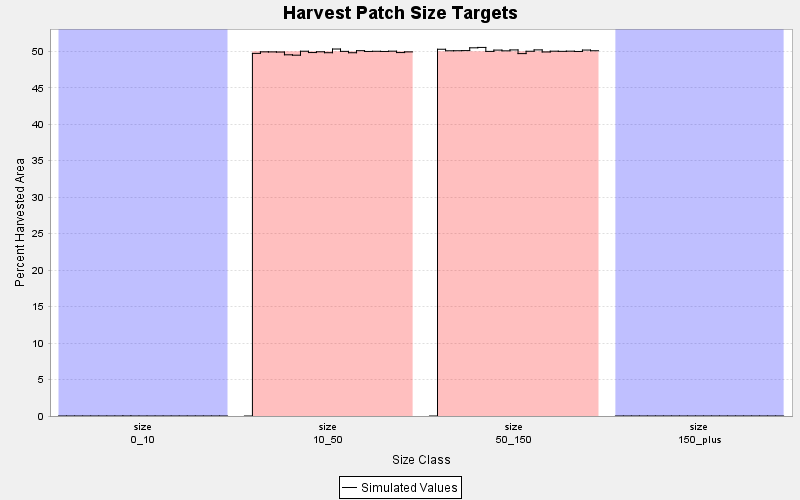
Patch targets are the workhorses of the spatial modeling system and can be used to represent many different types of policies. They are commonly used to define harvest opening size limits: too small may be economically inefficient; too large may violate environmental regulations. Patch targets are often used to implement 'Natural Range of Variation' policies, requiring a distribution of disturbed area across a range of size classes.
Patch targets are easy to set up: establish membership criteria, choose size classes, and set targets. Patch targets become goals in the overall objective function and may be traded off against other simultaneous goals, including multiple different patch targets at the same time.
Establish the Membership Criteria
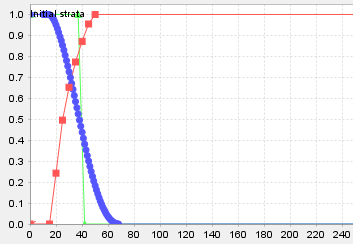
What identifies a stand as belonging to a patch? Was it harvested in the same planning period as a neighbour? Is it younger than a free-to-grow height? Is it in a particular seral stage condition? Use any combination of stand-level attributes to classify patch members.
Choose Patch Size Classes
Identify the range of patch size classes to track. Patchworks does all the work to identify dynamic structures on the landscape according to your criteria. Patch boundaries automatically change as management treatments are applied and stands grow.
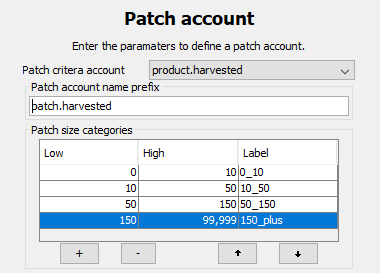
Set Targets
Set targets for the size classes of interest, and use these to control the minimum or maximum amounts in each class by area or frequency. Like all targets in the Patchworks system, values and weights can vary by planning period.
Edge Targets
Patchworks lets you build solutions that control the arrangement of forest types across the landscape and over time. Edge targets help control the arrangement of one forest type adjacent to another forest type. For example, ensure functional edge effects for wildlife by arranging forest types that support forage adjacent to forest types that support shelter.

Setting up edge targets is easy:
- Identify the different classes of forest types required for the functional effect.
- Define the edge contrast-weight matrix.
- Set up targets for the total edge contrast.
Like all other types of targets, multiple different edge targets may be simultaneously active, and each can be set in different zones in the forest.
Zonal Targets
Zonal targets control composition within a defined zone, the most common use being to limit the amount of disturbance within a specific geographic area. The Patchworks implementation of zonal targets is efficient and effective and can support many thousands of simultaneous targets for detailed control of your future forest.
Zonal targets can overlap one another without restriction, so there is no problem in modeling the types of complex and challenging policies facing forest managers today.
Visual Quality Objectives
Limit the amount of area in a visually disturbed condition within sensitive viewshed areas, with recovery thresholds based on site and forest cover characteristics.
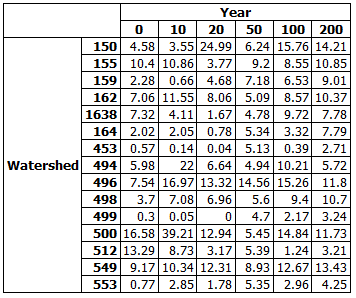
Watershed Protection
Measure and restrict the amount of hydrologically altered forest cover within catchment areas, or even get as detailed as individual riparian zones. Patchworks can easily handle thousands of zone targets.
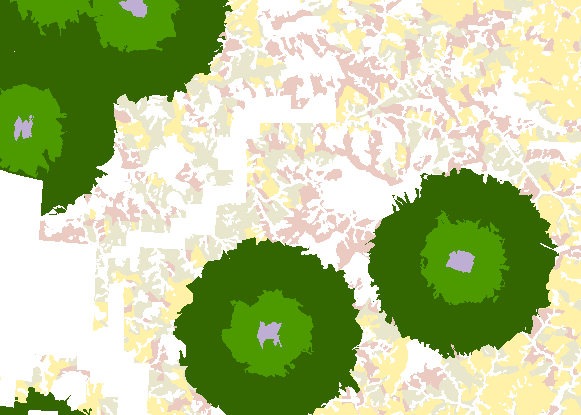
Habitat Protection Zones
Set up multiple protection levels based on distance from a sensitive feature. Patchworks will track, control, and report on each individual protected area, allowing for ultimate control.
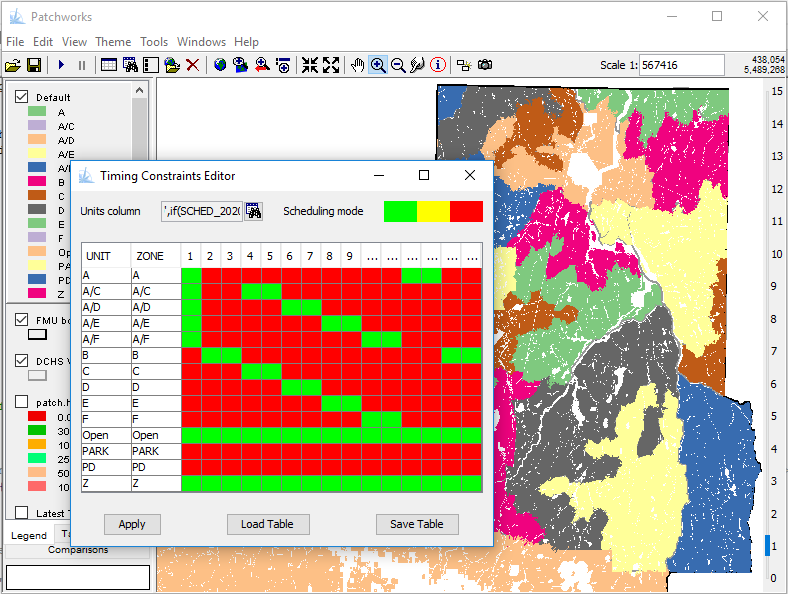
Timing Constraints
Some forest policies provide protective measures that restrict operations over long and variable time frames, such as for the protection of undisturbed forest within at-risk caribou ranges. Patchworks provides a convenient interactive tool to visually design timing constraint patterns.
Set up timing constraints by:
- Selecting the classifiers that identify the areas requiring restrictions.
- Using the Timing Constraints wizard to colour the areas and planning periods where the constraints apply.
- Clicking on the 'Apply' button.
Options are available to save and restore the timing constraint configuration to a file.
Manual Scheduling
Due to the lead times required, operational planners often layout and commit to pre-planned management treatments for the first few years of the management planning period. Use the manual scheduling option to lock these treatments and allow the Patchworks scheduler to design around them.

To apply manual scheduling:
- Prepare a CSV file containing the stand labels, treatment types, and treatment timings.
- Load the treatment schedule using the user interface or via a script.
- Apply a timing constraint to these stands to prevent the scheduler from altering the treatment.
Manual scheduling provides operational planners with a powerful tool to incorporate their realities into the strategic planning process. Select desired short-term activities and let the Patchworks model balance the long-term strategic goals.
Transportation Modeling
Transportation modeling is fully integrated within the Patchworks system and consists of two tightly coupled components: the choice of which processing facility to send a product to and the choice of which roads to travel on to get there. Use both of these elements to describe the nature of your business, and let Patchworks determine the best flows.
Road and destination targets are integrated and solved simultaneously with the other Patchworks targets. It is not a matter of determining harvest levels first and allocations second; Patchworks allows you to explore and find the best balance between investment, harvest, returns, and residual forest condition, with explicit spatial detail.
Road Network Targets
It is a truism that if you cannot access a forest stand, then you cannot manage it. Certainly, in most forests, it is not possible to harvest a stand without road access. Aspatial models that do not consider access timing risk unsustainable outcomes. Patchworks keeps track of the developed road network on your forest and will lay out future roads using a rational economic formulation that considers capital costs, haul distances, and the location of mature timber. This approach is highly dynamic and will trade off harvesting stands before or after their best economic rotation to achieve the best overall solution.
Road development, maintenance and hauling costs make up a significant part of the woodlands budget. Achieving a small percentage reduction in costs can more than pay for the entire forest modeling budget.
And the best part of the Patchworks road network formulation is that it works over long strategic time frames, along with all of the other sustainability targets. Use these features in combination to fully explore your strategic options.
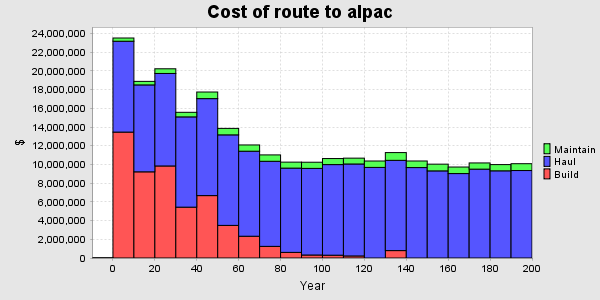
Conserve Capital Budgets
Get a solid handle on road construction requirements over time and examine all of your options. Use Patchworks to explore the trade-off between investment and wood supply.
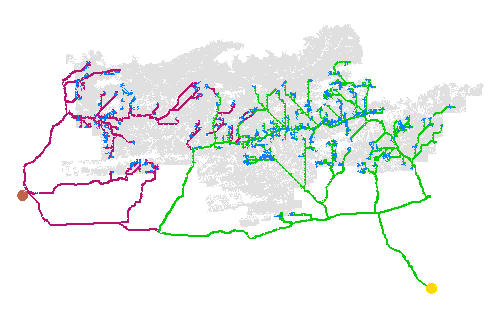
Control the Active Road Footprint
Reduce operating costs by using the road network formulation to control the extent of the currently active road footprint. Use the road network controls to cluster periodic harvests onto fewer access roads.
Measure and Mitigate Impacts
Use the road network formulation to explore measures to offset non-timber impacts. Use the detailed spatial road network to help forecast cumulative impacts across the landscape over time.
Multiple-Products to Multiple-Destinations
Patchworks lets you evaluate the flow of products from the landing to the processing facility. Multiple products may be generated at each site (hardwood logs, conifer logs, pulp wood), and multiple mills can accept different product specifications. Patchworks handles all of this with ease, allowing you to model realistic and complex regional wood supply arrangements and solving for flows that best meet your objectives. When coupled with the road model, Patchworks will independently allocate harvested products to the processing facilities to best achieve your suite of goals. Patchworks will dynamically adjust wood flow patterns over time across the managed area, considering the changing pattern of road access, maturing timber, and environmental requirements.
Not all wood has equal value, and maximizing the harvest may end up costing more. Use a full economic formulation to maximize your net revenues. Timber that is far from processing facilities will incur higher delivered costs and is best suited for a longer rotation. Stands close to the mill have lower delivered wood costs, higher mill-gate value, and are suitable for a shorter rotation. Rotation age determination is an automated part of the solution, based on your custom objectives.
Setting up multiple-product to multiple-destination formulations is easy:
- Identify the mill locations in the road network formulation.
- Identify the product requirements for each mill and set up accounts that track the harvest of those products.
- Set up accounts that connect the products to the allowable processing facilities.
- Set up targets for minimum quotas or sharing of production as appropriate.
Use the convenient interactive wizards to guide you through the account creation process.
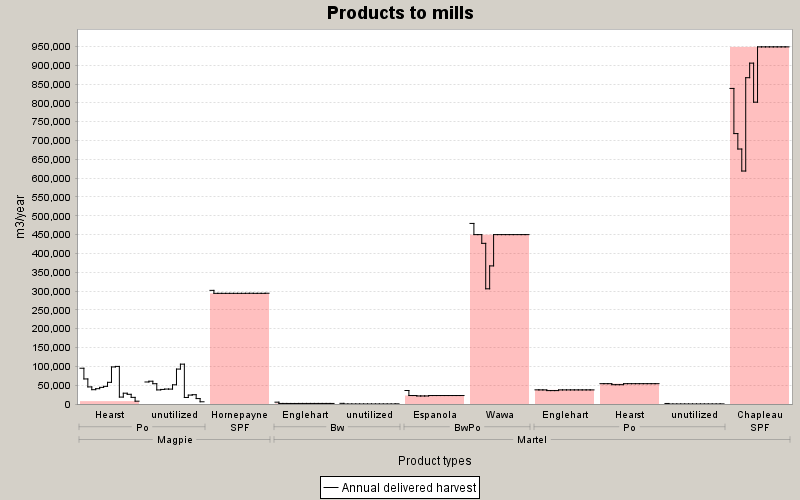
Efficient Collaboration
The Patchworks planning system has been designed with a number of features to help team members participate collaboratively and effectively in the planning process. The most important of these features are for team member engagement during the strategic planning phase and for meaningful and substantive input from operational planners during the refinement phase.
Strategic Planning
One of the most compelling features of Patchworks is the openness and transparency of the solutions it produces. It is easy to dig down through the results and confirm that the solution works on the ground, and is not just some abstract, not yet materialized proposition. Patchworks reporting can provide explicit information to help planning team members ensure that their concerns are addressed and to feel confident about the scenarios under consideration.
It is easy to share Patchworks outputs so that everyone on the team is up to date. By default, Patchworks will save results in linked HTML format, ready for sharing the ongoing series of modeling results on a website or shared folder.
Operational Refinement
Patchworks' best practices for management planning employ an operational refinement process. Once a strategic long-term management direction has been established, operational planners are provided with the spatially explicit spatial harvest sequence. The planners review the pattern and timing of harvest and consider factors that may not have been represented in the strategic model (cruise data, field inspections). The operational planners make adjustments to the short-term sequence to defer or delete some treatments and move forward or add others. The revised short-term schedule is loaded into the model, locked to prevent scheduling changes, and the model is solved again to rebalance the long-term goals. This process is repeated until a viable short-term and sustainable long-term solution is produced.
Powerful Scripting
Patchworks can be used as a visually interactive system, and it can also run batch processes. Interactive mode is perfect for prototyping and exploring, with many tools and inspectors to help fully understand what is going on. Batch mode is better for production because the scripts involved provide for repeatable outcomes as well as documenting exactly what steps were taken.
Interactive mode is supported by a rich user interface, featuring a full set of inspectors to view the inputs and simulation state, and a comprehensive set of controls to adjust management objectives. Patchworks works seamlessly with the rest of the operating system, allowing drag-and-drop to load files and cut-and-paste to transfer results.
Patchworks also comes with BeanShell — a powerful object-oriented scripting language — and a comprehensive API that provides full control over the modeling environment and user interface. BeanShell scripts can be used to prepare data sets, configure simulation parameters, run unattended analysis, interact with other third-party modeling tools, and much more. Don't worry if you are not a hard-core coder: most of the visual configuration tools have options to display the equivalent scripting actions, so preparing a batch script can be as easy as copying and pasting a few lines of code.
Comprehensive Reports
Reports summarize and extract simulation data while the model is solving or after the simulation has finished. The ReportWriter provides a range of reporting templates that can be quickly configured, as well as crosstab and pivot table reports that can be customized to the exact shape of your query.
Most reports provide results as HTML pages containing summary data tables, a summary chart, and a link to the raw data in CSV format. Reports are linked together with hyperlinks so that simulation results can be perused with a standard web browser. The standard action when a simulation finishes is to write out a folder containing all reports. This folder can be shared with planning team members, allowing them to dig into results without requiring additional licenses.
Here are a few of the commonly used report types, out of the many templates that are available:
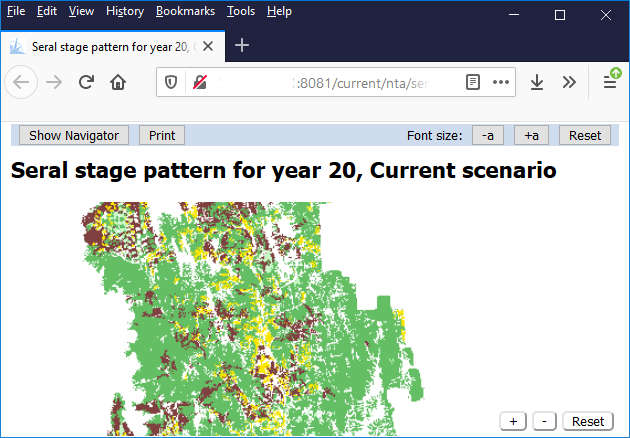
Map Report
Map reports provide a quick and easy visual format to present landscape views of simulation results. Select map layers and adjust symbology in a MapViewer window, and then use the Map Report wizard to create the report.
Pivot Table Report
Pivot table reports use an intuitive drag-and-drop visual metaphor to configure complex queries. They are easy to use due to the quick visual feedback and automatic provision of categories.
Table Query Report
Extract data for use in other models using a table query report. Table query reports subset and transform simulation data and save the results as CSV or dBase data files for easy export and import.
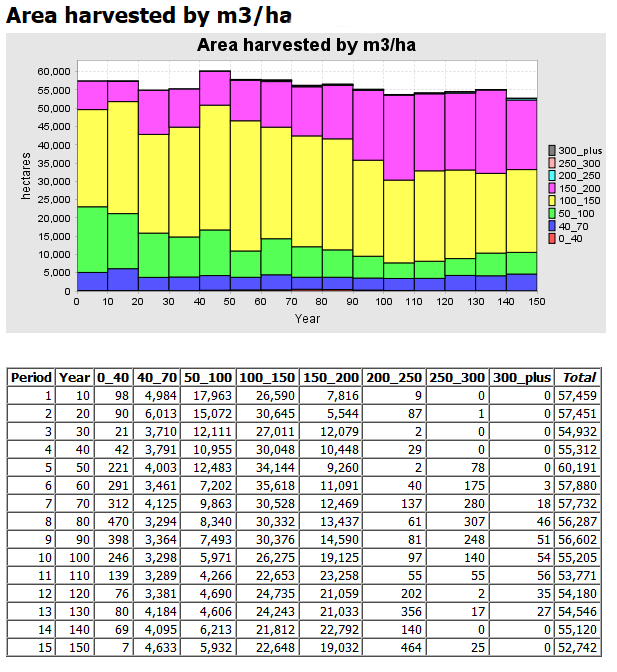
General Purpose Templates
General purpose templates are flexible and easy to configure for many different types of queries, and they automatically provide charts, tables, and easily accessible raw data.
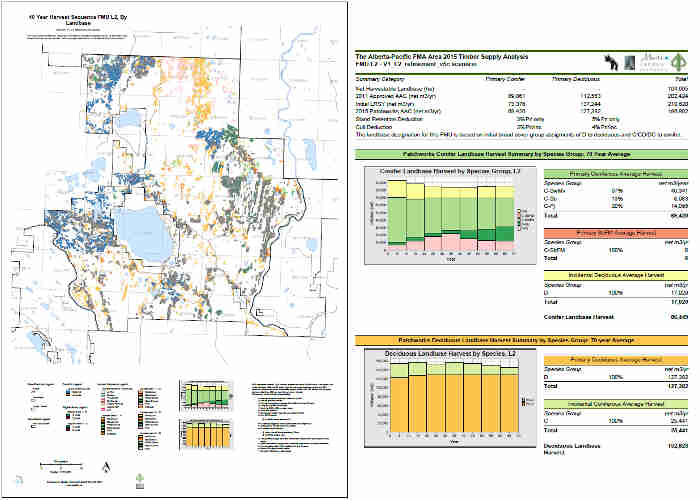
Layout Report
Layout reports offer exceptional configurability and are exceptionally cost-effective for large production projects. Arrange map layers, charts, tables, text, and logos over multiple pages of output. The PDF output format conveniently allows for high-quality vector mode zooming, panning, selective enabling of map layers, and interactive area and distance measuring. Embed attribute data to allow clients to use point-and-click to drill down into detailed data.
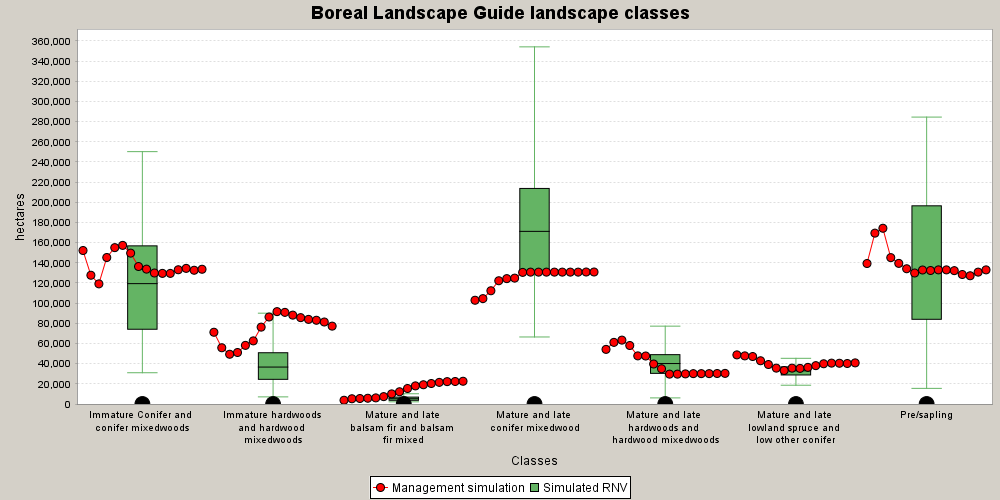
Box And Whisker Report
Box and whisker reports display the simulated values while providing the context of minimum, maximum, mean, and quartile values.
A Full Toolbox
Patchworks comes fully loaded with lots of tools to build models, run simulations, and post-process results. Process spatial files with tools to subset, dissolve, and join layers. Split polygons according to specified criteria. Join tables, recalculate columns, compute convex hulls, build topological relationships, and more. Some tools are simple time savers, while others are fully-fledged applications in their own right. All of these tools can be invoked from easy-to-use wizards or reusable batch scripts. At each step of the way, these tools are designed to work seamlessly and save you time.
Here are just a few of the tools that are available:
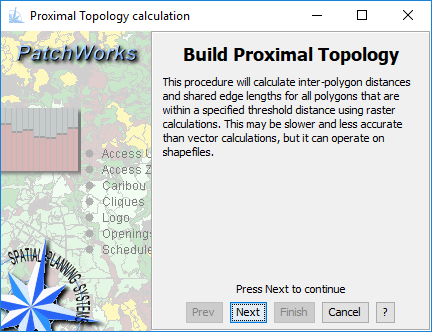
Build Proximal Topology
Proximal topology includes neighbours that are within a specified separation distance as well as immediately touching polygons. Proximal topology is required to assess contiguity during patch structure assessment. Most GIS programs do not provide this analytical operator, or it requires following a complicated processing stream. The Patchworks tool is simple to use and built right in.
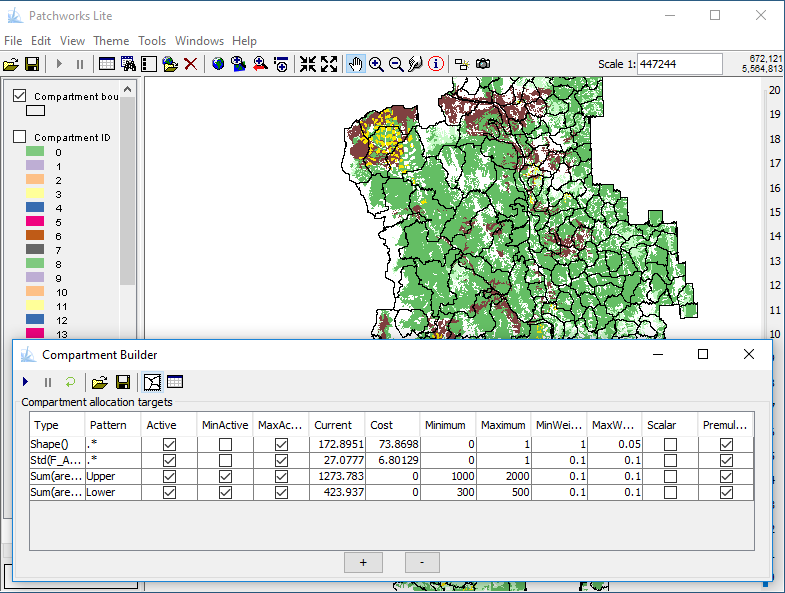
Compartment Builder
Automatically subdivide your landscape using the interactive Compartment Builder tool. Use predefined zones and linear features to define the hard boundaries, and then set the targets for compartment size and homogeneity. The Compartment Builder will produce a shapefile of zone boundaries.
Intelligent Dissolve
Intelligent dissolve is the perfect tool for dealing with polygon slivers. Set the criteria for precious boundary requirements and targeted polygon size, and let the tool group your fragments into manageable pieces. Use the results with the MatrixBuilder to ensure no loss of accuracy from the dissolve operation.
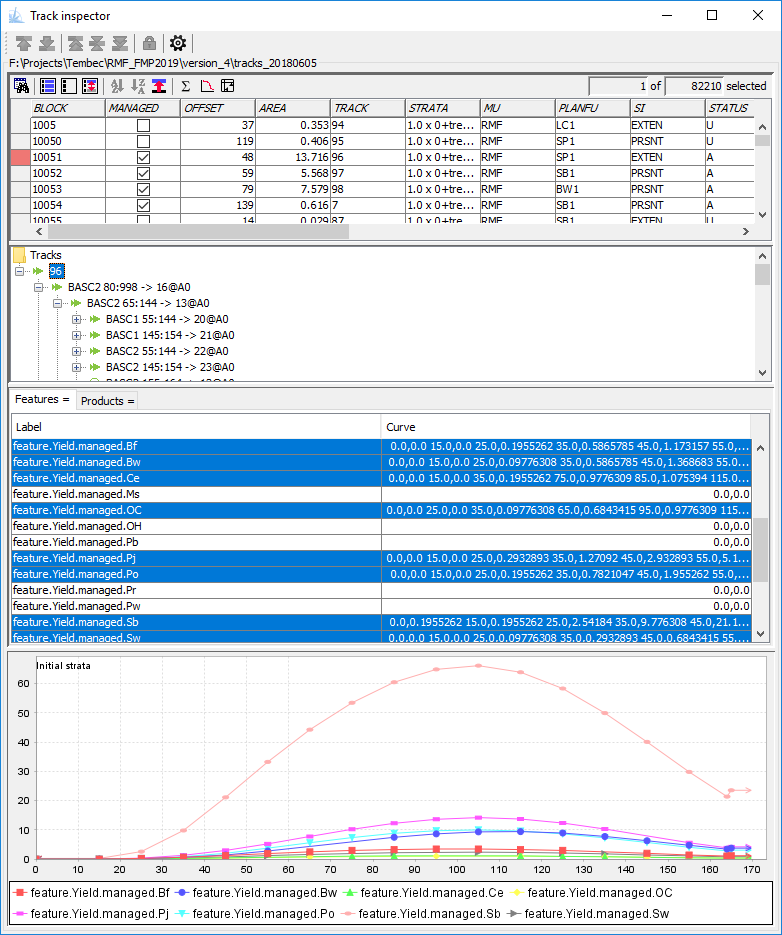
Inspect Stand Dynamics
Dive into your stand dynamics data sets with the Track Inspector. Use this tool to browse through your forest inventory and visually confirm that the yield curves, stand attributes, available treatments, and future responses have been defined correctly. You can also extract charts and tables to help document your data package.
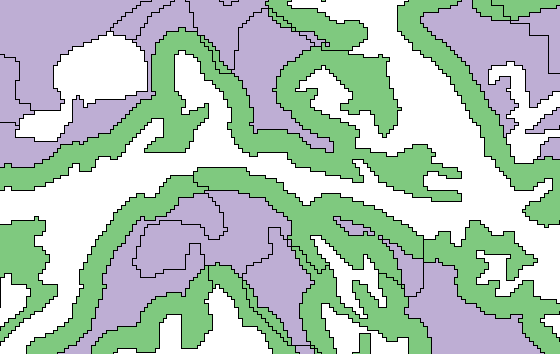
Interior Core Area
The interior core area tool provides a fast calculation of core area boundaries using a raster-based buffer-out/buffer-in algorithm. The tool can operate on the live Patchworks modeling structures, thus avoiding the necessity of exporting spatial data to an external GIS program. Interior core calculations are immediately available for use with other Patchworks tools and reports.
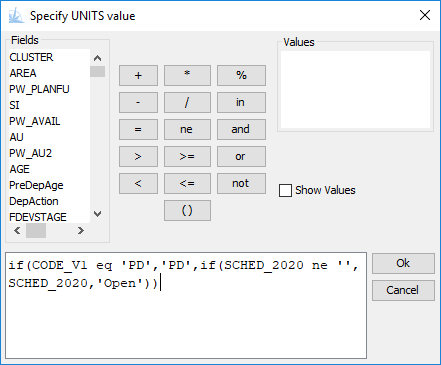
Powerful Query Language
The Patchworks Query Language is used by all the tools throughout the Patchworks system to select records and calculate values. The language has a regular syntax and a full set of data types, operators, and functions. The syntax has been designed to be familiar and easy to learn, and a query builder wizard makes it the easiest of all.